Permutations II
Given a collection of numbers, nums, that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations in any order.
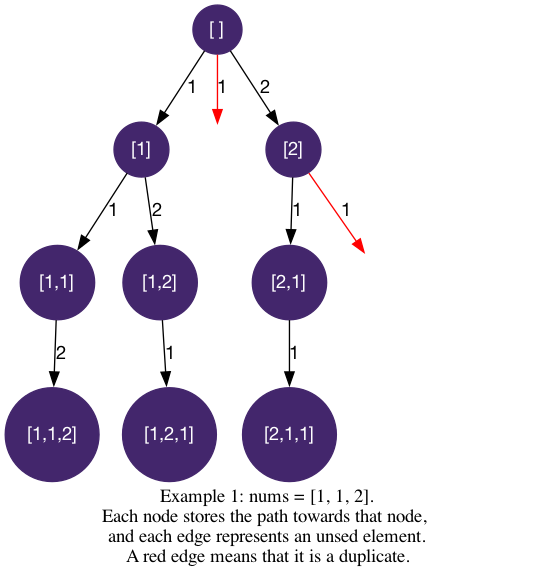
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output:
[[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 8-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
Solution
Let's fill in the logic for backtracking1:
path_length: indicates the number of elements inpathused: an array storing the status of whether an element is used.is_leaf:path_length == len(nums), whenpath_lengthis the same asnums's length.get_edgesandis_valid: all elements that are unused (used[i]==Flase).
In the implementation, we use an array used to store the whether an element has been used or not.
Everytime we use a number, we add it into the path and we mark it used (used[idx] = True).
Since there are duplicate values, let's apply methods in Deduplication to deduplicate the results.
we want to sort the nums array so that duplicate elements are consecutive, and only proceed when the current element is the first of its occurrance.
Implementation
def permuteUnique(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
used = [False] * len(nums)
ans = []
nums.sort()
def dfs(path_length, path):
if path_length == len(nums):
ans.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(0, len(nums)):
if used[i]: continue
if(i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and not used[i-1]): continue
path.append(nums[i])
used[i] = True
dfs(path_length + 1, path)
used[i] = False
path.pop()
dfs(0, [])
return ans
Ready to land your dream job?
Unlock your dream job with a 2-minute evaluator for a personalized learning plan!
Start EvaluatorWhich of these pictures shows the visit order of a depth-first search?

Recommended Readings
LeetCode Patterns Your Personal Dijkstra's Algorithm to Landing Your Dream Job The goal of AlgoMonster is to help you get a job in the shortest amount of time possible in a data driven way We compiled datasets of tech interview problems and broke them down by patterns This way we
Recursion Recursion is one of the most important concepts in computer science Simply speaking recursion is the process of a function calling itself Using a real life analogy imagine a scenario where you invite your friends to lunch https algomonster s3 us east 2 amazonaws com recursion jpg You first
Runtime Overview When learning about algorithms and data structures you'll frequently encounter the term time complexity This concept is fundamental in computer science and offers insights into how long an algorithm takes to complete given a certain input size What is Time Complexity Time complexity represents the amount of time
Want a Structured Path to Master System Design Too? Don’t Miss This!